
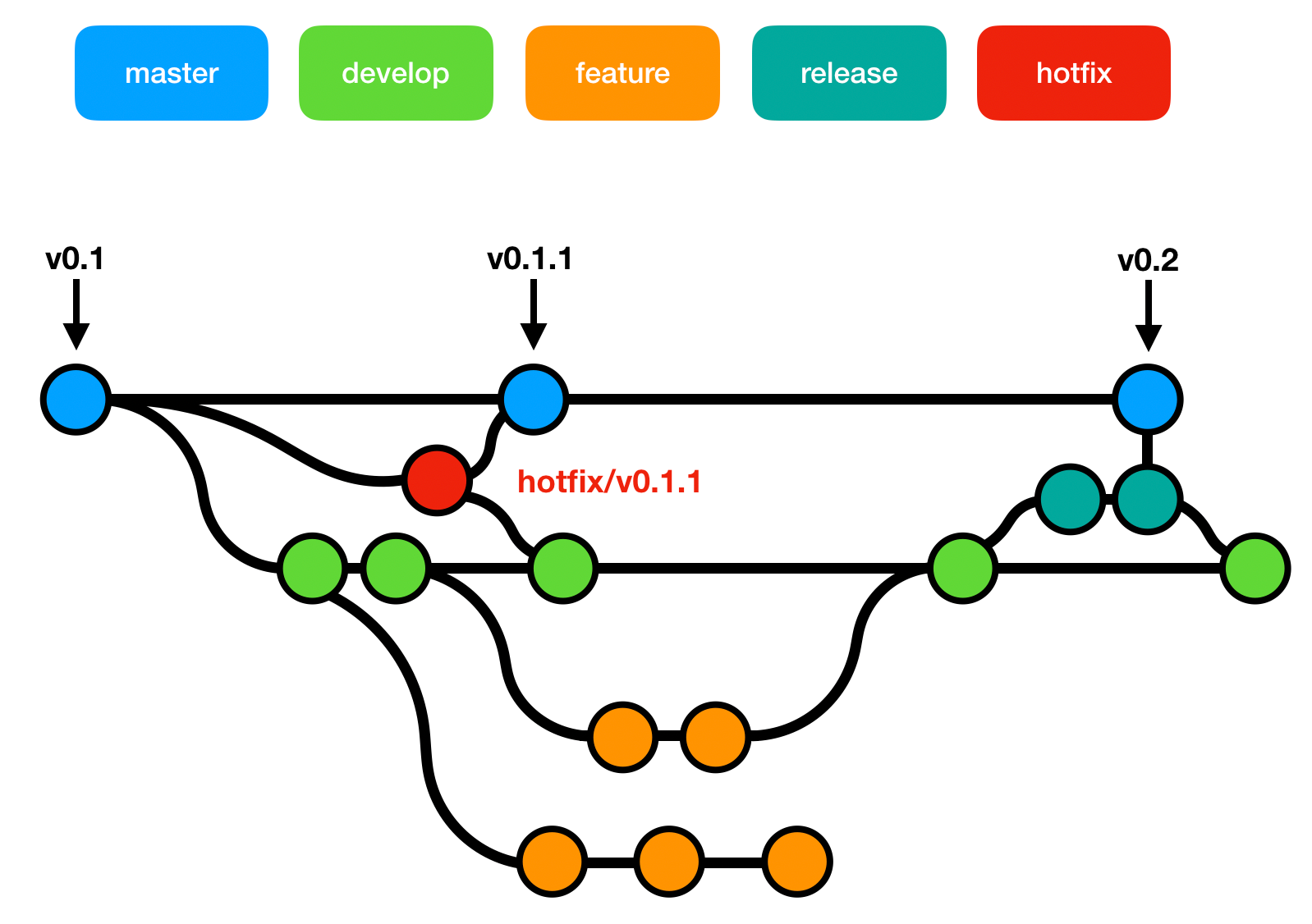
In almost every organization that's running small to large-size projects under a source control, like Git, the need to branch out specific updates, or commits, is inevitable. Introduction to managing your Git branches It is important that you read every section carefully and check the other posts linked in the introduction section in case more information is needed on separate topics on Git. This will not only create a local branch, but also set up a "tracking relationship" between the two branches, making sure that pulling and pushing will be as easy as "git pull" and "git push".In this post, renaming, changing and removing a Git branch will be explained in details by commands on Git Bash. When Git cannot find the specified name as a local branch, it will assume you want to check out the respective remote branch of that name: $ git switch remote-branch If you want to check out a remote branch (that doesn't yet exist as a local branch in your local repository), you can simply provide the remote branch's name. If, in one go, you also want to create a new local branch, you can use the "-c" parameter: $ git switch -c new-branch This will make the given branch the new HEAD branch. The most common scenario is to simply specify the local branch you want to switch to: $ git switch other-branch Simply double-click a branch in the sidebar to make it the new HEAD branch - or choose a branch from a list. In case you are using the Tower Git client, switching branches becomes easy as pie. This can be helpful if you want to often and quickly jump between two branches. When specifying just the "-" character instead of a branch name, Git will switch back to the last checked out branch. Using the "-discard-changes" flag will discard any of your current local changes and then switch to the specified branch.
However, if you have local modifications that would conflict with the switched-to branch, Git would abort the switch. As a general rule, your working copy does NOT have to be clean before you can use "switch". Switch to the specified branch and discard any local changes to obtain a clean working copy. You can also specify a starting point (either another branch or a concrete revision) if you don't provide any specific starting point, the new branch will be based on the current HEAD branch. Using the "-c" flag, you can specify a name for a new branch that should be created. The name of a new local branch you want to create. If you specify the name of an existing local branch, you will switch to this branch and make it the current "HEAD" branch.īut you can also specify a remote branch: in that case, Git will create a new local branch based on that remote branch and set up a tracking relationship. The name of a local or remote branch that you want to switch to. It has a very clear and limited purpose: switching and creating branches! Important Options

The "switch" command provides a simple alternative to "checkout". The problem with "checkout", however, is that it's a very versatile command: you can not only use it to switch branches, but also to discard changes, restore files, and much more. It's relatively new (added in Git v2.23) and provides a simpler alternative to the classic "checkout" command.īefore "switch" was available, changing branches had to be done with the "checkout" command. The "switch" command allows you to switch your current HEAD branch.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
